Diodes Basics
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are used.
A diode is a basic device for all remaining electronic devices those are like transistors , amplifiers etc. first of all we have to know the diode operation properly. It will be helpful for knowing other concepts easily. The combination of back to back diode assumes to be as a transistor and a transistor along with passive components will acts an amplifier, this way by knowing the diode operation is very useful.
Different types of Diodes:
Diode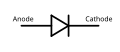
Light Emitting Diode(LED)
Photo diode
Schottky diode
Transient voltage suppression diode
Tunnel diode
Varicap 
Zener diode
Typical diode packages in same alignment as diode symbol. Thin bar depicts the cathode.

Diode operation:
Simple Diode:
The diode operates in two regions those are ON and OFF regions. The above diode is connected properly with an active source of a circuit then it allows the current through it.In other direction it can't allow the current flow. so that the diode will operate in forward (F)region and disabled in reverse(R) region. i.e acts as short circuit in F region and open circuit as R region. The graphical representation is shown in below.
V-I Characteristics:


























No comments