A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
 |
transistors
|
Configuration details:
Transistor is a three terminal device. we already known those terminals are emitter,base,and collector, for every port network we need two ports for giving input and two ports for obtaining output. Hence one of the terminal of a transistor is made common to the input and output circuits. Thus there are 3 types of configurations for operation of a transistor.
Those are common base,common emitter and common collector types.
common base configuration:
 |
| Basic NPN common base circuit (neglecting biasing details) |
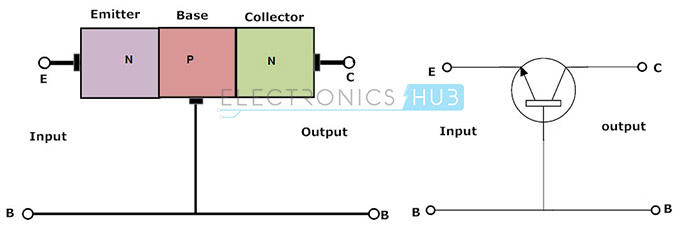 |
CB configuration
|
common emitter configuration:
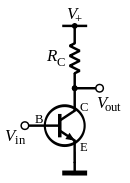 |
| Basic NPN common-emitter circuit (neglecting biasing details) |
 |
CE Configuration
|
common collector configuration:
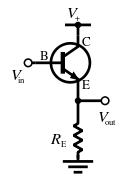 |
| Basic NPN common collector circuit (neglecting biasing details) |
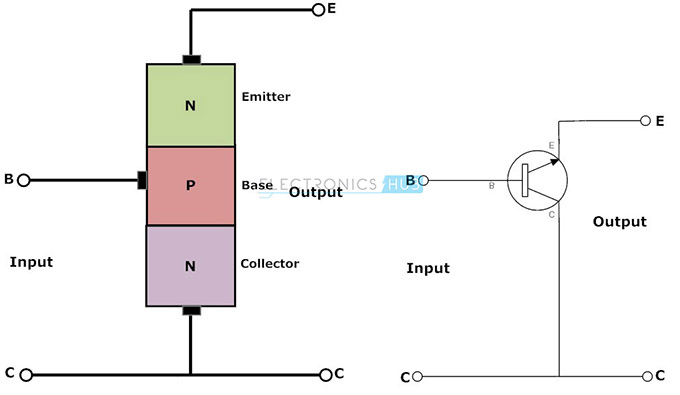 |
| CC configuration |
we will learn about these concepts in detail in next sections.




























No comments